Choosing the right connector is crucial for product performance.
Selecting the wrong type can lead to connection failures and design setbacks.
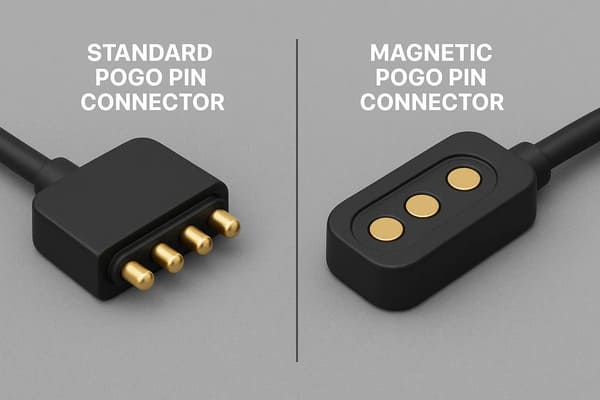
Let’s clarify the distinctions between standard and magnetic pogo pin connectors.
The core difference lies in the connection mechanism.
Standard pogo pins use only spring force for contact, requiring precise manual alignment.
Magnetic pogo pins integrate magnets to create a self-aligning feature.
This ensures a secure, quick-mating attachment that simplifies operation and prevents accidental disconnections.

Understanding these fundamental differences is key to selecting the optimal connector solution for your specific device or system.
Let’s delve deeper into each type to help you make an informed decision.
What is a Standard Pogo Pin Connector?
Need a dependable connection but feel unsure about the fundamentals?
Standard pogo pins are widely used, but knowing their basic structure and function is vital for successful implementation.
A standard pogo pin connector is an interconnect device utilizing a spring-loaded pin within a barrel.
The pin compresses upon contact, and the internal spring applies constant, steady pressure to maintain a reliable electrical connection.
This simple mechanism allows for repeated mating cycles and accommodates variations in alignment.
To bridge the understanding of their practical use, let’s explore how these components come together in real-world scenarios.
Knowing the design details can help in selecting the right connector for specific needs.
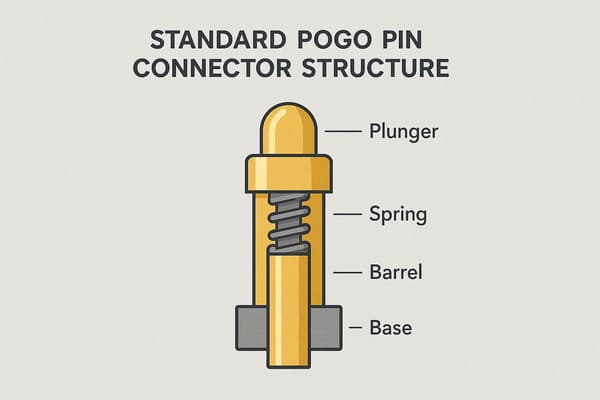
Understanding Standard Pogo Pin Design Details
Standard pogo pins, often called spring-loaded connectors, are the foundation of many electrical connections in modern devices.
Their design is simple yet effective.
- Core Components:
- Plunger: The moving part that makes contact.
It’s typically gold-plated for excellent conductivity and durability. - Barrel: A small tube, usually made of brass alloy, that houses the spring and plunger.
- Spring: Provides the necessary force to maintain consistent contact pressure between the plunger and the target contact pad.
- Plunger: The moving part that makes contact.
These components in pogo pin connectors ensure a robust electrical connection despite varying surface conditions.
They are ideal for board-to-board links, battery contacts, and test fixtures, offering durability and cost-effectiveness with precise alignment.
What Makes Magnetic Pogo Pin Connectors Unique?
Frustrated by tricky alignments or connections that easily detach?
Magnetic pogo pin connectors offer an innovative solution, but what exactly gives them their edge over standard types?
A magnetic pogo pin connector uniquely integrates magnets to create a self-aligning and self-guiding connection.
This "snap-to-connect" action ensures the pins mate correctly without precise manual effort.
The magnetic force provides a secure attachment that resists accidental disconnection, enhancing reliability and simplifying the user experience.

This inherent magnetic feature provides more than just a convenient connection.
It unlocks several practical advantages that improve device durability, user safety, and overall performance in a variety of demanding applications.
Exploring Key Magnetic Spring Loaded Pin Connector Advantages
The defining feature of a magnetic pogo pin connector is the addition of magnetic force to the connection process.
This is typically achieved by incorporating strong permanent magnets, often neodymium, into the connector housing or around the pogo pins themselves.
- Key Advantages:
- Effortless Connection: Magnets actively guide the two connector halves together, requiring minimal user effort.
- Self-Alignment: The magnetic pull ensures pins align correctly with contact pads, reducing the risk of damage from misalignment.
- Secure Mating: The magnetic force provides strong retention, keeping the connector securely mated even with movement or vibration.
- Blind Mating Capability: Users can easily connect the parts without precise visual alignment, ideal for hard-to-reach spots or quick connections.
Magnetic assistance enhances the usability of magnetic spring-loaded pin connectors, particularly in smartwatches and laptops for charging.
Their reliable connections are increasingly vital in medical, industrial, and automotive applications for seamless performance.
How Do Connection Mechanisms Differ?
Connection integrity is non-negotiable in electronics.
Failing to grasp how standard and magnetic pogo pins engage can result in poor performance, intermittent faults, or complete device failure.
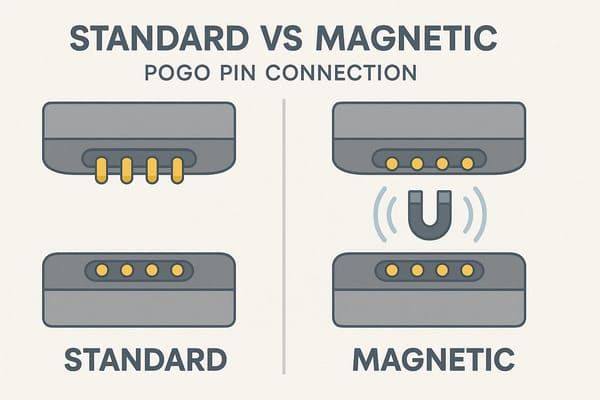
Standard pogo pins rely entirely on mechanical spring force for contact and require precise manual alignment.
In contrast, magnetic pogo pins add integrated magnets to this mechanism.
This addition automates alignment and provides a stronger, self-securing connection, reducing reliance on user precision while enhancing retention.
This core mechanical difference creates significant variations in practical performance.
To make an informed choice, it’s crucial to understand how each approach impacts durability, user convenience, and overall connection reliability.
Comparing Standard vs. Magnetic Pogo Pin Connection Mechanisms
The primary distinction lies in how the connection is initiated and secured.
Standard pogo pins require the user to physically align the connector halves correctly so the spring-loaded pins engage their corresponding pads.
Magnetic pogo pin connectors use magnetic attraction to actively pull the connector halves into the correct alignment, significantly reducing the need for precise manual positioning.
| Feature | Standard Pogo Pin Connector | Magnetic Pogo Pin Connector |
|---|---|---|
| Alignment | Manual; Requires precision | Magnetically assisted; Self-aligning |
| Retention | Spring force; Friction fit | Spring force + Strong Magnetic attraction |
| Ease of Use | Requires careful mating | Snap-to-connect; Highly user-friendly |
| Vibration Res. | Moderate | Generally higher due to magnetic hold |
| Blind Mating | Difficult | Easy |
This variation impacts usability and reliability of connections.
Magnetic guidance in magnetic pogo pin connector designs accelerates mating, reduces wear from misalignment, and offers resistance to disconnection caused by vibration.
Which Applications Suit Each Type Best?
Specifying the wrong pogo pin type can lead to redesigns, costing valuable time and resources.
Understanding the ideal use cases for standard and magnetic connectors helps optimize your design from the start.
Standard pogo pins are utilized for fixed, internal applications like board-to-board links or test interfaces where alignment is pre-set.
Conversely, magnetic pogo pins are designed for external, user-facing ports requiring frequent connection, such as for charging.
Their magnetic self-alignment is crucial for ensuring reliability and ease of use.

Determining Optimal Pogo Pin Connector Applications
Choosing between standard and magnetic pogo pin connectors depends heavily on the end-use environment and user interaction.
-
Ideal Scenarios for Standard Pogo Pins:
- Internal PCB-to-PCB connections where the connection is permanent or rarely disturbed.
- Battery contacts within sealed device enclosures.
- High-density test beds and programming jigs.
- Applications where minimizing cost is a primary driver.
- High-current applications are possible with appropriate design.
-
Ideal Scenarios for Magnetic Pogo Pins:
- External charging ports for consumer electronics (e.g., wearables, tablets).
- Data transfer ports requiring quick connect/disconnect cycles.
- Medical devices needing reliable and easy connections.
- Connectors for modular systems or accessories.
- Applications in challenging environments needing secure, easily manageable connections.
- High-current magnetic options are also available.
For static internal connections, a standard pogo pin connector often suffices.
For frequent use or added durability against disconnections, a magnetic pogo pin connector design offers better reliability and ease of mating.
Conclusion
In summary, standard pogo pins provide reliable connections using spring force, suited for stable internal uses.
Magnetic pogo pins add magnets for effortless, secure, self-aligning connections, ideal for user interfaces.
Selecting the right type hinges on your application’s specific requirements.
